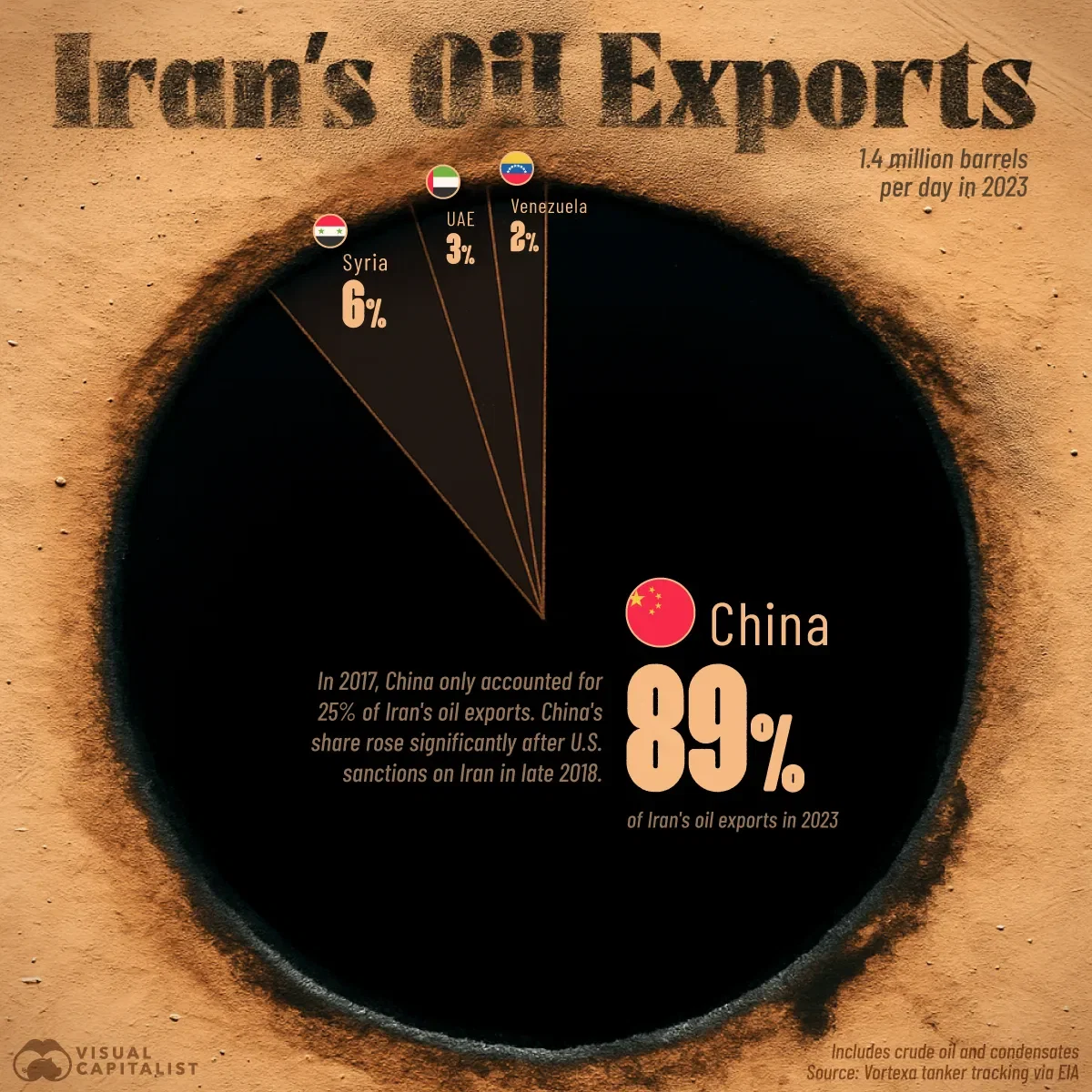
theguardian.com
Dramatic changes in energy industry and EVs reducing fossil fuel use, but shipping, aviation and industry a long way from net zero
@olliemilmanFri 9 Feb 2024 12.00 GMT
Humanity has made some uneven progress in reducing our addiction to fossil fuels – but there remain three areas of our lives in which we are notably not on track to kick the habit over the next 30 years, according to a new analysis.
Record levels of investment in clean energy (solar has been called the cheapest source of electricity in history by the International Energy Agency) and a decline in coal-powered generation means less and less of the world’s power will come from fossil fuels between now and 2050, the analysis from Rhodium shows.
Similarly, the blossoming electric vehicle market is going to drive down emissions from cars and trucks, with global oil consumption for on-road vehicles set to drop by 50% over the next three decades, the forecast finds.
But even with these dramatic changes reshaping two of the world’s hungriest consumers of fossil fuels, emissions are still a long way from hitting net zero by 2050, as scientists say they must if dangerous global heating – spurring worsening heatwaves, floods, droughts and more – is to be avoided.https://interactive.guim.co.uk/uploader/embed/2024/02/archive-zip/giv-13425ZCBwhBxEyLin/
A major reason for this is the stubborn, ongoing carbon pollution from three areas: aviation, shipping and industry.
.https://interactive.guim.co.uk/uploader/embed/2024/02/archive-zip/giv-13425v3zDOTaHHQGz/
There is currently no widespread alternative to jet fuel or ship diesel, meaning steady or even rising fossil fuel use as developing countries’ economies grow. A range of industrial processes – such as cement-making and the production of plastic – will collectively fail to meaningfully cut carbon-intensive fuels by 2050, too.
“We’ve made a lot of progress in the last few years – wind and solar are really poster children of success and electric vehicles are at a turning point now,” said Hannah Pitt, associate director at Rhodium, which made the projections based on anticipated policies until 2050.
“That makes up a good chunk of emissions but there is much less progress in other sectors. With aviation and shipping, there’s just not as much innovation and no clear cost-effective alternatives to fossil fuels.
“And then we have industrial processes that make up a huge fraction of emissions and each require their own tools and innovations to bring that down, and emissions are staying stubbornly high.”
All told, global fossil fuel use will likely flatten or decline by mid-century before starting to grow again due to rising energy demand in various parts of the world, according to the report’s projections. Gas will lead the way, rising significantly in use even as oil and coal decline.https://interactive.guim.co.uk/uploader/embed/2024/02/archive-zip/giv-13425v3zDOTaHHQGz/
Pitt said we are still a long way from breaking our dependence on fossil fuels in everything from switching on a light at home, to driving a car, to getting an Amazon package delivered, to flying to a holiday destination.
“The success with renewables and EVs shows it can be done, but it really will take a lot of different policies and innovations. There’s no one solution,” said Pitt.
“This is a good reminder that climate change touches every piece of our economies, and it needs solutions to each of those areas. There is a lot of work to do.”