What’s the issue?
Climate change and modern slavery are linked closely together in a vicious circle.
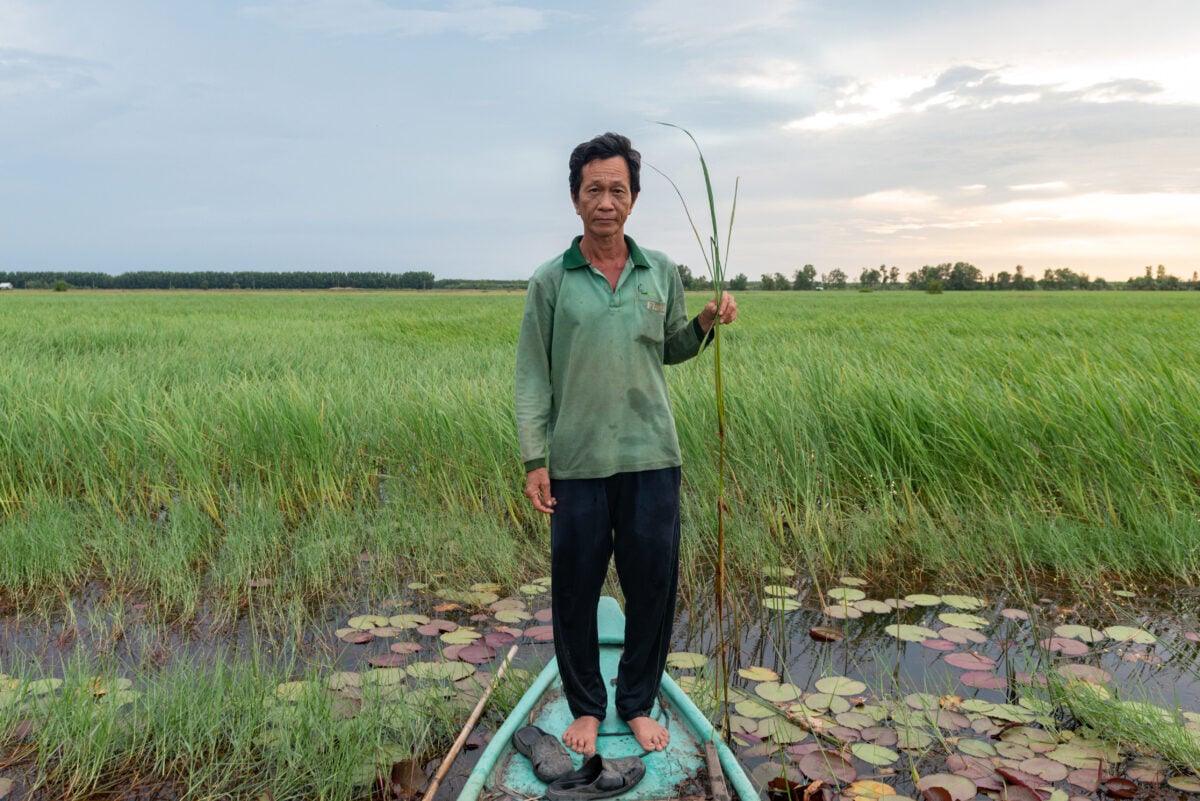
Climate-induced disaster, environmental degradation and growing scarcity of resources are affecting many communities, driving millions of people into poverty and forcing many to migrate in search of work, food or safety. In many cases, victims of the climate emergency will be left more vulnerable to forms of modern slavery, including human trafficking, forced labour and child slavery.
Three of the ways that climate change and modern slavery are linked:
- When people are forced to migrate, they face greater risks of human trafficking and forced labour. People who lose their livelihoods, income and ties to their community are often made vulnerable to exploitation, and in the worst cases, modern slavery, as they are forced to migrate. By 2050, the World Bank estimates that more than 143 million people will have been forced from their homes in sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia and Latin America because of climate change
- The same industries that drive climate change leave people vulnerable to forced migration. Extractive industries and agricultural businesses in particular contribute to the emissions that drive climate change, while also profoundly damaging the land and water that ordinary people rely upon. This pushes many more people into poverty and forces them to leave their homes and communities, making them more vulnerable to people traffickers and at risk of slavery
- Many victims of the climate emergency are exploited by businesses that contribute to the problem. Many of the people forced into migration by the climate emergency find themselves trafficked into forced labour, some within the very industries that are degrading the environment – completing a vicious circle in which climate change drives, and is driven by, modern slavery
Tiếp tục đọc “Climate change and modern slavery are linked:”




 We believe in the free flow of information
We believe in the free flow of information
