Tóm lại, ở các tộc người ấy vì nam giới “không có quyền, nên không có trách nhiệm”. Cho nên, những bà vợ của họ “càng có quyền càng khổ”. Lối giải thích này tạo một ấn tượng sai lạc rằng trong các cộng đồng mẫu hệ thì “chị em ta” là nhất, “bọn đàn ông” chẳng có ký lô nào! Tai hại hơn, nó biến những người đàn ông thiếu ý thức trách nhiệm, bê tha rượu chè, làm khổ vợ con thành những người đáng được cảm thông, và biến chế độ mẫu hệ thành kẻ tội đồ!
Trong khi sự thật là dù trong chế độ mẫu hệ hay phụ hệ thì quan hệ, đời sống và hạnh phúc gia đình tốt hay xấu, trước hết là do ở con người. Nếu nói trong chế độ mẫu hệ giới đàn ông vì “không có quyền nên không có trách nhiệm” thì chẳng lẽ dưới chế độ phụ hệ, tất cả đàn ông, với quyền lực trong tay, đều rất có tinh thần trách nhiệm đối với cuộc sống gia đình?
Với những cách hiểu, cách giải thích, cách đánh giá như vậy, sẽ không phải là điều lạ nếu có ai đó trong những người hoạch định, thừa hành pháp luật, chính sách có ác cảm và có cách đối xử sai lầm đối với chế độ mẫu hệ của các tộc người thiểu số. Chẳng thế mà trong Nghị định số 32/2002/NĐ-CP ngày 27/3/2002 của Chính phủ quy định việc áp dụng Luật Hôn nhân và gia đình đối với các dân tộc thiểu số, người ta đã đưa tập quán “Người con bị bắt buộc phải mang họ của người mẹ” của chế độ mẫu hệ vào danh mục “Các phong tục, tập quán lạc hậu về hôn nhân và gia đình cần vận động xoá bỏ” (Phụ lục B).
Theo chúng tôi, dù chỉ là “vận động xoá bỏ” chứ không phải là “nghiêm cấm”, quy định đó cũng thể hiện một cái nhìn kỳ thị và xâm phạm truyền thống văn hoá của các tộc người theo mẫu hệ.
(Trích Nam quyền trong chế độ mẫu hệ ở Việt Nam)
- Nam quyền trong chế độ mẫu hệ ở Việt Nam
- Danh mục các tập quán lạc hậu về hôn nhân và gia đình
Tiếp tục đọc “Kỳ thị và xâm phạm truyền thống văn hoá của các tộc người theo mẫu hệ” →
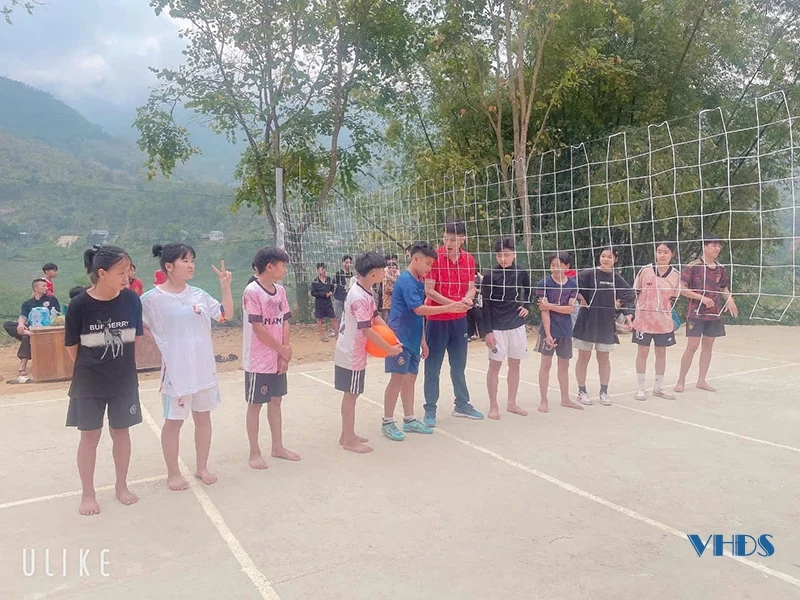


 Trường PTDT Bán trú THCS Trung Lý (Mường Lát) tổ chức cho học sinh thi bóng chuyền.
Trường PTDT Bán trú THCS Trung Lý (Mường Lát) tổ chức cho học sinh thi bóng chuyền.