An ICIJ investigation examines networks of companies, people and business practices that draw profit from cross-border labor trafficking and sex trafficking.
By Michael Hudson Image: Rocco Fazzari / ICIJ June 12, 2023
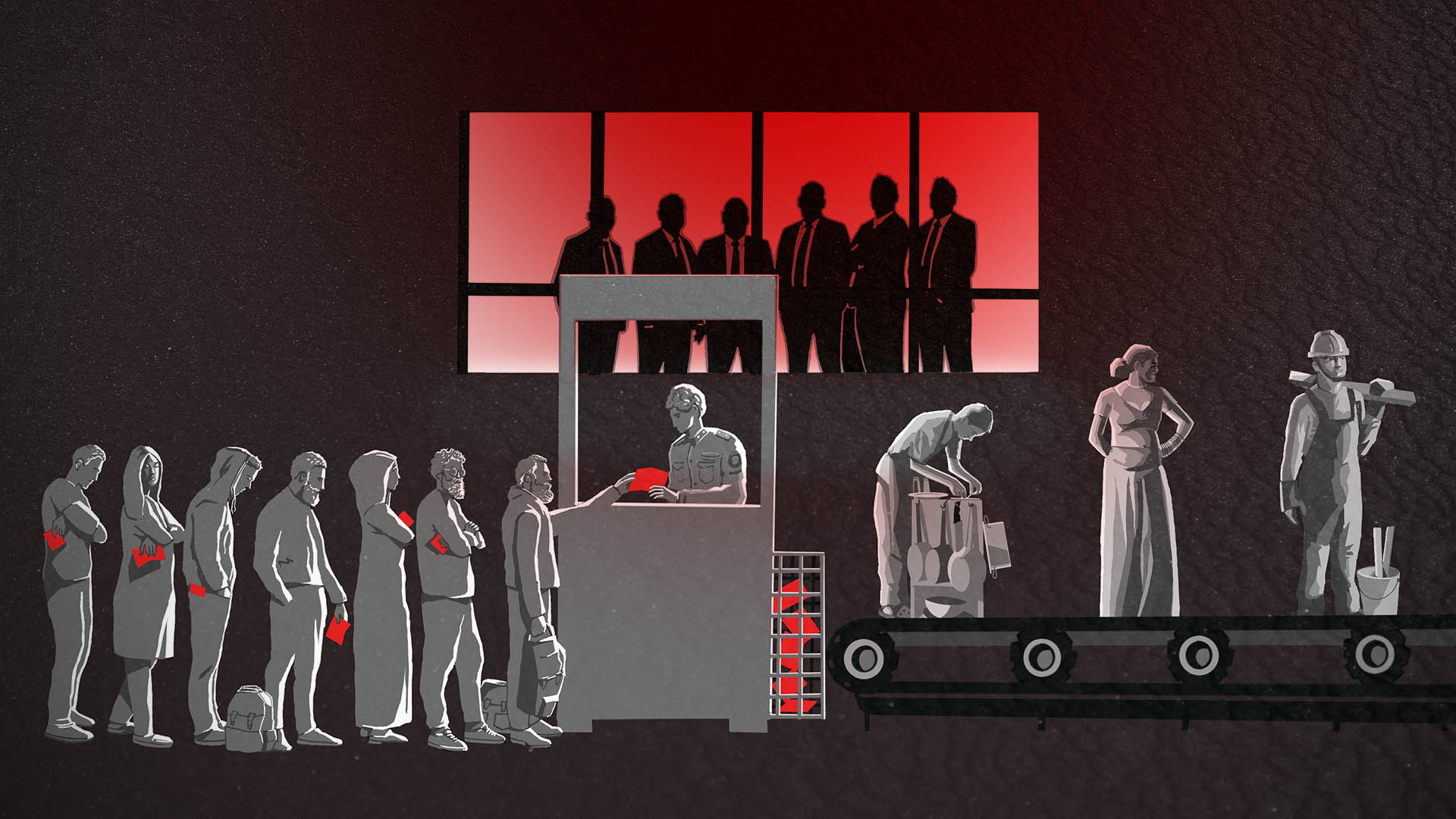
On any given day, the United Nations estimates, nearly 28 million adults and children around the world are trapped in jobs that are so oppressive that they amount to modern slavery or human trafficking.
They are forced to work long hours for little or no pay, toiling on farms and construction sites, in sweatshops and restaurants, as janitors and, in some cases, sex workers. They are exploited by recruiters and employers who use their poverty, isolation and immigration status against them, often threatening them with violence, arrest or deportation or ensnaring them in debts they struggle to repay.
A new investigation by the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists and other media partners has begun examining human trafficking in Asia, Africa, the Middle East and the United States.
The investigation, Trafficking Inc., focuses on two forms of human trafficking: labor trafficking and sex trafficking. Both involve using force, fraud or coercion to induce someone to work or provide a service.
ICIJ and its reporting partners are working to bring to light untold stories of hardship and abuse suffered by trafficked people — and expose the networks of companies, individuals and business practices that set the traps and profit from them.
The investigative team includes journalists from ICIJ, Reuters, NBC News, WGBH Boston, The Washington Post, Arab Reporters for Investigative Journalism, the Philippine Center for Investigative Journalism and the Investigative Reporting Program at the University of California, Berkeley.
Stories released by the partnership in late 2022 have won several accolades, the New York Deadline Club’s prize for business investigative reporting and a selection as one of the year’s top investigations in the Arab world.
Stories released include articles by ICIJ, The Post, NBC and ARIJ that revealed that many foreign workers for defense contractors on U.S. military bases in the Persian Gulf have been targets of abusive labor practices — including illegal recruiting fees that force migrants who are paid as little as $1 an hour to work for years before they’ve paid off their debts.
Other stories released in 2022 included pieces by WGBH that revealed flaws in U.S. protections for trafficked workers and the failure of Massachusetts authorities to punish labor traffickers who prey on vulnerable workers.
A story copublished in June 2023 by ICIJ and Reuters examined sex trafficking between Nigeria and other African nations and the United Arab Emirates. The story was based on court records and other documents and interviews with 25 African women who described being lured to the UAE by traffickers along with dozens of interviews with humanitarian workers, investigators, Nigerian government officials and others with knowledge of sex trafficking in the Emirates.
More stories will be published by ICIJ and media partners in the coming weeks.
- Leak to us
- Contact reporter
Do you have a story about corruption, fraud, or abuse of power?
ICIJ accepts information about wrongdoing by corporate, government or public services around the world. We do our utmost to guarantee the confidentiality of our sources.
Human trafficking is said to be the world’s fastest growing criminal enterprise. In 2014, the United Nations’ International Labor Organization reported that, between them, labor and sex trafficking produce an estimated $150 billion in illicit profits annually. At that time, the organization said 21 million people were working under conditions of forced labor. A report released in September 2022 by the International Labor Organization and a nonprofit group, Walk Free, estimated that, as of 2021, the number of people working under forced labor conditions had grown to 27.6 million.
Keeping workers physically and emotionally isolated is a method of control in many trafficking cases. Employment agents or employers often take away passports and cell phones and tell workers that if they try to leave they will be arrested.
Some recruiters and employers use threats of violence or actual violence to trap and control trafficked workers. But coercion in human trafficking doesn’t always involve direct threats of physical harm. Often workers are lured into well-laid traps that ensnare them in large debts for recruitment fees or take advantage of their precarious immigration status.
In some countries it is a crime to break an employment contract. Authorities often don’t care if the contract was fraudulent or the employer abuses workers.
Under the “kafala” system in Jordan, Lebanon and most Persian Gulf countries, for example, employers exercise wide control over migrant workers’ freedom of movement and legal status. The Council on Foreign Relations, a New York-based think tank, notes that there’s growing recognition the system is “rife with exploitation.”
Beyond the kafala system, immigration laws in many countries — including the United States — leave migrant workers vulnerable to labor abuses.
The toll that labor trafficking takes on workers is wide-ranging and powerful. Along with economic exploitation, they can be exposed to physical and sexual violence, infectious diseases, hunger, unsanitary living arrangements and dangerous working conditions. Surveys of workers who have been trafficked find high levels of depression and post-traumatic stress disorder.
War, disease, disasters, global warming, poverty and inequality serve as “push factors,” prompting vulnerable workers to seek out new jobs and new lives in new places.
Amid the global Covid-19 pandemic, the United Nations reported that human traffickers had adjusted their business models to the “new normal” created by the disease, especially through “the abuse of modern communications technologies.”
“Most importantly,” the U.N. said, “the pandemic has exacerbated and brought to the forefront the systemic and deeply entrenched economic and societal inequalities that are among the root causes of human trafficking.”
Frequently asked questions about the Trafficking Inc. investigation
What sort of trafficking does this investigation cover? Are there any leaked files? How can I send ICIJ tips? These questions and more, answered.
By ICIJ
Image: Rocco Fazzari / ICIJ
June 12, 2023

The International Consortium of Investigative Journalists began publishing its Trafficking Inc. investigation in October 2022, and will continue publishing stories in 2023 in partnership with media outlets from around the world over the coming months.
What is the Trafficking Inc. investigation?
Trafficking Inc. is an investigation into human trafficking in Asia, Africa, the Middle East and the United States. ICIJ and its media partners are working to bring to light untold stories of hardship and abuse suffered by trafficked people — and expose the networks of companies, individuals and business practices that set the traps and profit from them.
What sort of trafficking does this investigation cover?
Trafficking Inc., focuses on two forms of human trafficking: labor trafficking and sex trafficking. Both involve using force, fraud or coercion to induce someone to work or provide a service. These forms of trafficking frequently involve people being exploited by recruiters and employers who use their poverty, isolation and immigration status against them — often threatening them with violence, arrest or deportation or ensnaring them in oppressive debts.
What are some of the major findings of Trafficking Inc. so far?
Some of the stories published in 2022 revealed that many foreign workers for defense contractors on U.S. military bases in the Persian Gulf have been targets of abusive labor practices — including illegal recruiting fees that force migrants who are paid as little as $1 an hour to work for years before they’ve paid off their debts. Other stories produced by the reporting partnership in 2022 highlighted flaws in U.S. protections for trafficked workers and the failure of Massachusetts authorities to punish labor traffickers who prey on vulnerable workers.
A story copublished in June 2023 by ICIJ and Reuters examined sex trafficking between Nigeria and other African nations and the United Arab Emirates. The story was based on court records and other documents and interviews with 25 African women who described being lured to the UAE by traffickers along with dozens of interviews with humanitarian workers, investigators, Nigerian government officials and others with knowledge of sex trafficking in the Emirates.
ICIJ and its media partners will be publishing more stories over the coming weeks.
What news outlets are involved in this reporting partnership?
The investigative team includes journalists from ICIJ, Reuters, NBC News, WGBH Boston, The Washington Post, Arab Reporters for Investigative Journalism, the Philippine Center for Investigative Journalism and the Investigative Reporting Program at the University of California, Berkeley.
