CNA Few countries are better prepared against China threatening their rare earth supplies than Japan, says David Fickling for Bloomberg Opinion.

David Fickling 09 Jan 2026 05:59AM(Updated: 09 Jan 2026 09:30AM)
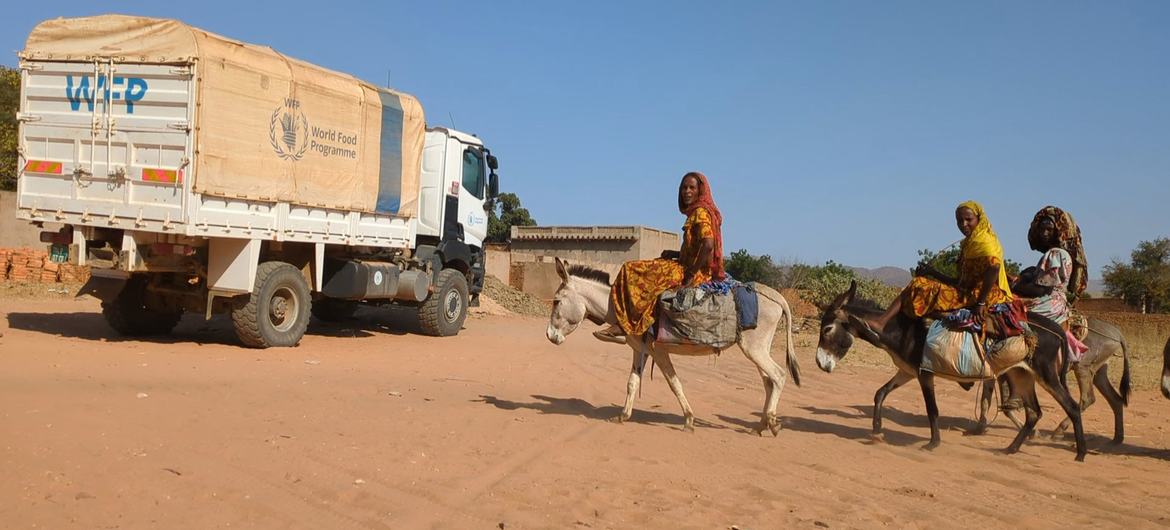
SYDNEY: To a hammer, every problem is a nail. If your most potent means of geopolitical leverage is threatening supplies of high-strength magnets, rare earth elements will always be the solution.
That’s the latest approach Beijing is taking in its dispute with Tokyo sparked by comments from Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi about the possibility of military conflict over Taiwan. Exports of all items with potential military applications to Japan will be immediately banned, China’s Ministry of Commerce said on Tuesday (Jan 6).
The most obvious victim of this threat will be rare earth magnets made with the elements neodymium and praseodymium, and increasingly spiced up with rarer samarium, dysprosium and terbium. They’re used everywhere from charging cables to the switchgear in wind turbines to motors powering electric vehicles, missile guidance systems and aircraft flaps.
Tiếp tục đọc “China is overplaying its rare earth hand in Japan”
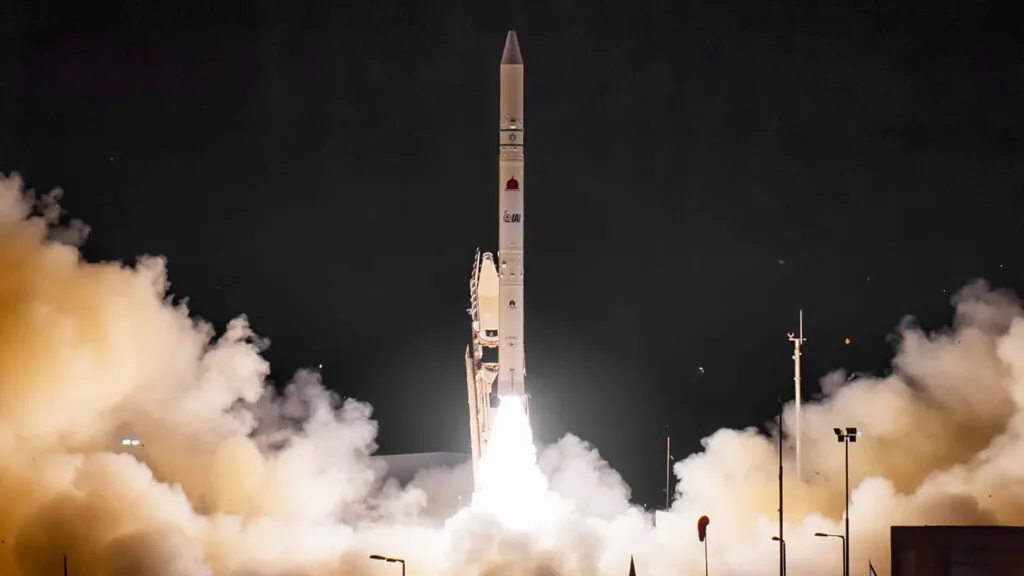






 Israeli space launch vehicle Shavit sends a military intelligence satellite into space in March 2023. The same Shavit rocket can launch ballistic missiles, including the nuclear-capable, three-stage Jericho III intermediate-range ballistic missile. The Jericho III reportedly has a range exceeding 4,000 kilometers, enough to reach all of Iran, Pakistan, Europe, and western Russia. Israel has not acknowledged the existence of its nuclear weapon arsenal despite being widely known. (Credit: Israel Defense Ministry)Share
Israeli space launch vehicle Shavit sends a military intelligence satellite into space in March 2023. The same Shavit rocket can launch ballistic missiles, including the nuclear-capable, three-stage Jericho III intermediate-range ballistic missile. The Jericho III reportedly has a range exceeding 4,000 kilometers, enough to reach all of Iran, Pakistan, Europe, and western Russia. Israel has not acknowledged the existence of its nuclear weapon arsenal despite being widely known. (Credit: Israel Defense Ministry)Share


