chatthamhouse.org Research paper Published 20 April 2020 ISBN: 978 1 78413 391 7

Royal Navy Vanguard Class submarine HMS Vigilant returning to HMNB Clyde after extended deployment. The four Vanguard-class submarines form the UK’s strategic nuclear deterrent force. Photo: Ministry of Defence.21st century. Researchers at Chatham House have worked with eight experts to produce this collection of essays examining four contested themes in contemporary policymaking on deterrence.
- Summary
- 1. Introduction
- Human Rationality and Nuclear Deterrence
- Nuclear Deterrence Destabilized
- Connecting the Dots: US Extended Nuclear Deterrence and Denuclearization of the Korean Peninsula
- Australia and Extended Nuclear Assurance
- The Risks Posed by Emerging Technologies to Nuclear Deterrence
- Deterrence Below the Threshold of Collective Defence: Is It Possible?
- ‘Blurring the Lines’: Nuclear and Conventional Deterrence
- The Problem of Blurring Conventional and Nuclear Deterrence
- 10. Editors’ Concluding Observations
- About the Authors
- About the Editors
- Acknowledgments

 Photojournalist Yoshito Matsushige, in front of the first image he took at Miyuki-bashi Bridge, a little over two hours after the United States dropped a nuclear bomb on Hiroshima. He took a total of 5 images, the only recorded evidence of that day that changed history. (Photo by John van Hasselt/Corbis via Getty Images)Share
Photojournalist Yoshito Matsushige, in front of the first image he took at Miyuki-bashi Bridge, a little over two hours after the United States dropped a nuclear bomb on Hiroshima. He took a total of 5 images, the only recorded evidence of that day that changed history. (Photo by John van Hasselt/Corbis via Getty Images)Share In November, 115 states voted in favor, eight voted against, and 44 abstained from voting on a resolution adopted by the General Assembly’s First Committee that examines the possible risks of integrating AI into nuclear weapons systems. Image: depositphotos
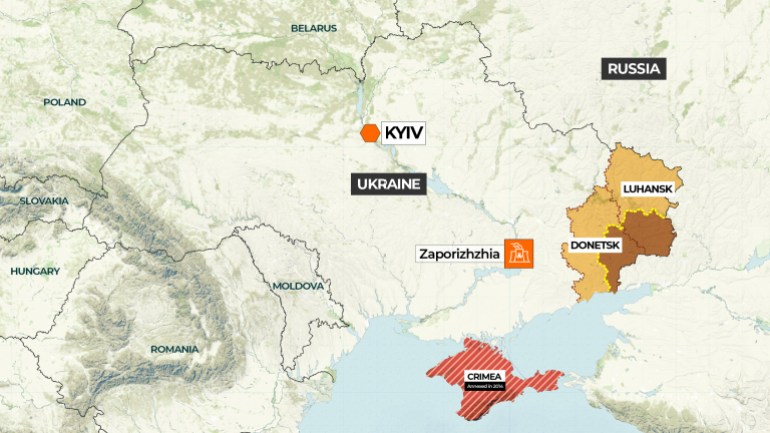
In November, 115 states voted in favor, eight voted against, and 44 abstained from voting on a resolution adopted by the General Assembly’s First Committee that examines the possible risks of integrating AI into nuclear weapons systems. Image: depositphotos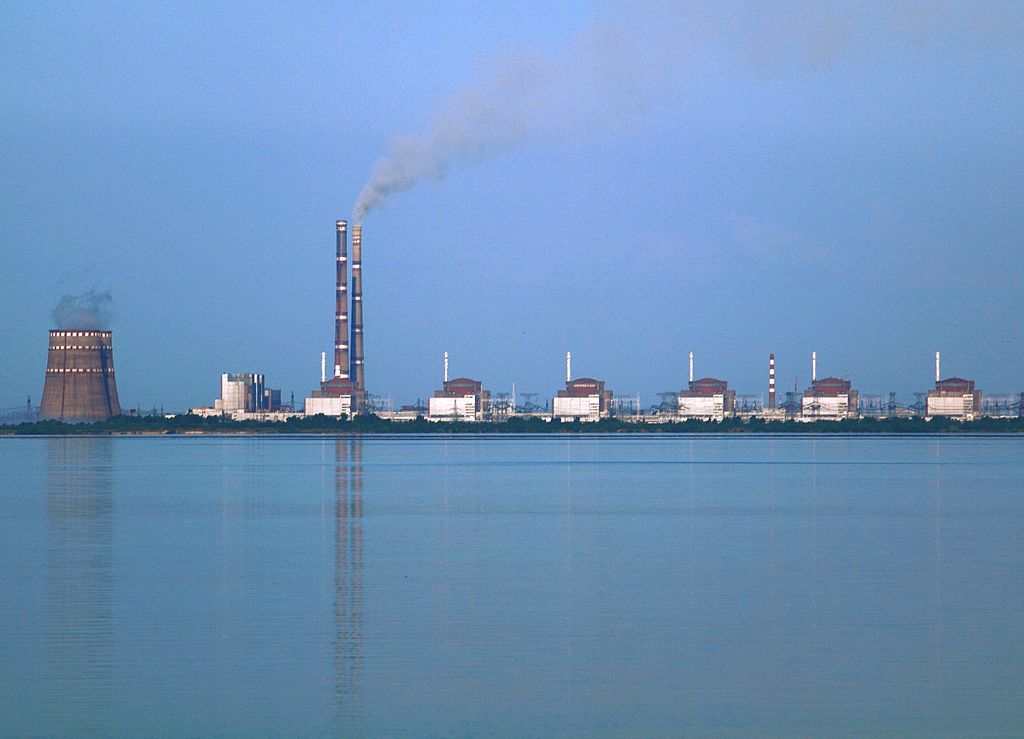  Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant in southern Ukraine. The two tall smokestacks are at a coal-fired generating station about 3km beyond the nuclear plant. Photo credit: Ralf1969 via Wikimedia Commons.
Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant in southern Ukraine. The two tall smokestacks are at a coal-fired generating station about 3km beyond the nuclear plant. Photo credit: Ralf1969 via Wikimedia Commons.