By YANNICK PETERHANS and ANIRUDDHA GHOSALUpdated 9:02 AM GMT+7, March 5, 2025Share
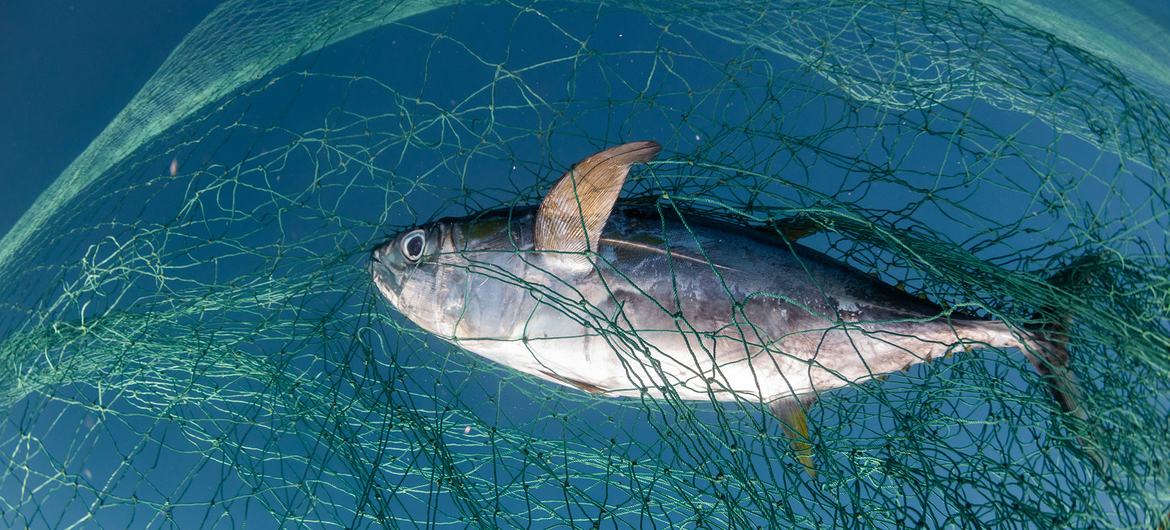
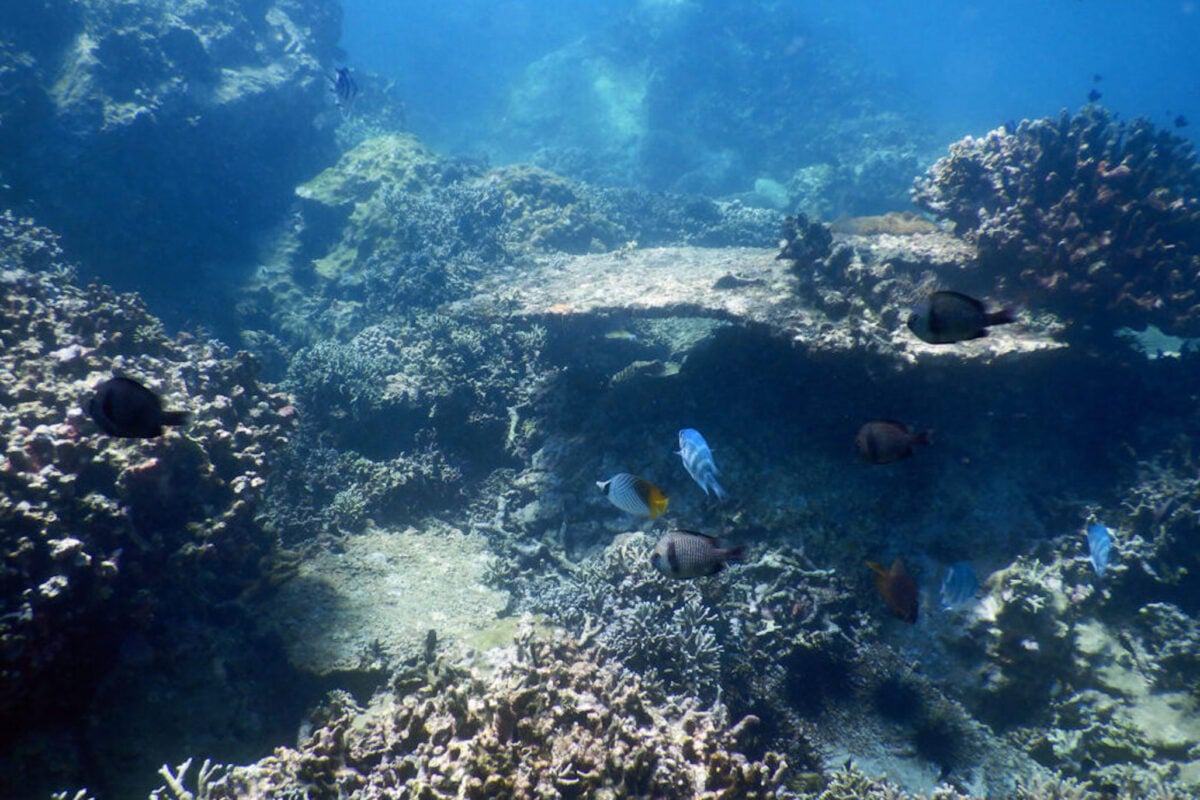
NHA TRANG, Vietnam (AP) — The gentle waves off the coast of central Vietnam’s Nha Trang obscure an open secret: The life-giving coral reefs below are dying. The waters are eerily devoid of fish. The bounty of the ocean is coming to an end.
This is why Binh Van — who fished in these waters for over two decades — now charters his boat to Vietnamese tourists wanting to experience the thrill of fishing in the deep waters of the South China Sea. But there is only squid, which is flourishing in oceans warmed by climate change, to catch. His passengers don’t mind as the boat moves away from Nha Trang’s twinkling beach resorts. But Van is pensive.
It wasn’t always like this. There was a time when he’d catch 70 kilograms (154 pounds) of fish, like tuna and grouper, in one night. He can’t make money on the squid.
“Now I usually go home empty-handed,” he said.
Tiếp tục đọc “Coral reefs in Vietnam face collapse. Can conservation efforts turn the tide?”